We are historically recognized for our brazing pastes and powders.
Traditionally, brazing filler metals are available under solid forms (sheets, wires, etc.). However, this makes it difficult to automatize and slow for large scale production. To overcome this issue, NASA developed the brazing paste technology during the 1960’s. This technology enables dispensing easily the filler metal, along with a flux, in a paste form.
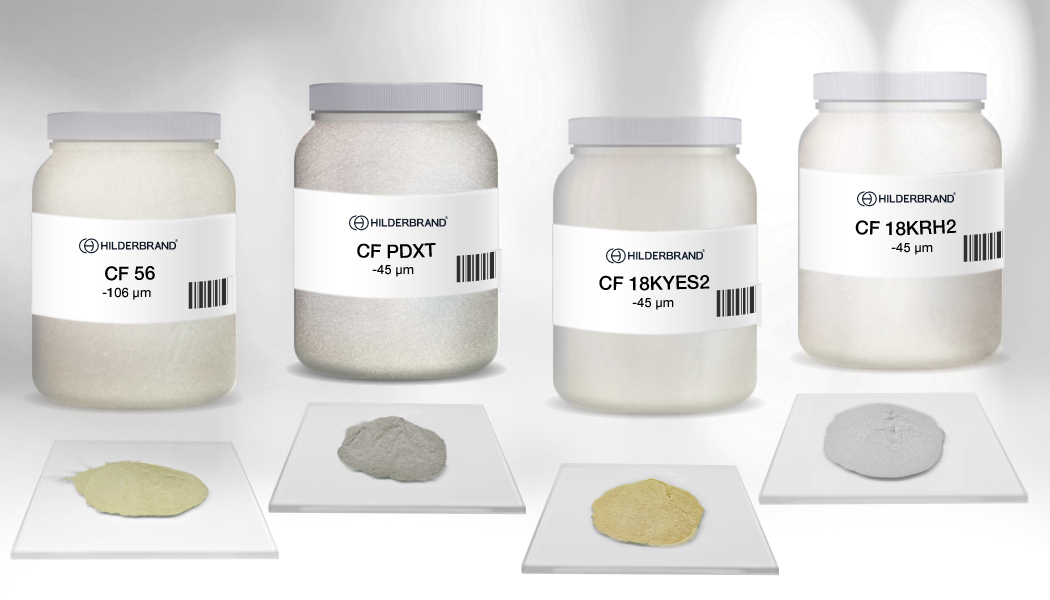

Powder
Hilderbrand has produced precious metal powders by gas atomization for over 45 years. Brazing filler metals are atomized while molted under high pressure inert gas in order to produce fine spherical particles. The output powder is then processed to keep only the required fractions. Depending on the application, we produce different range of our premium quality powders.
Binder
A wide range of binders is used for the production of paste solder. Depending on the desired behavior of the paste, our technical team chooses the appropriate binder. The quantity of powder is adapted. Our pastes are therefore custom-made to meet the requirement of the customer’s application. In conclusion, our binders are both useful for brazing pastes and powders.
- Paste rheology
- Stability-Consistency (thermal, sedimentation, etc.)
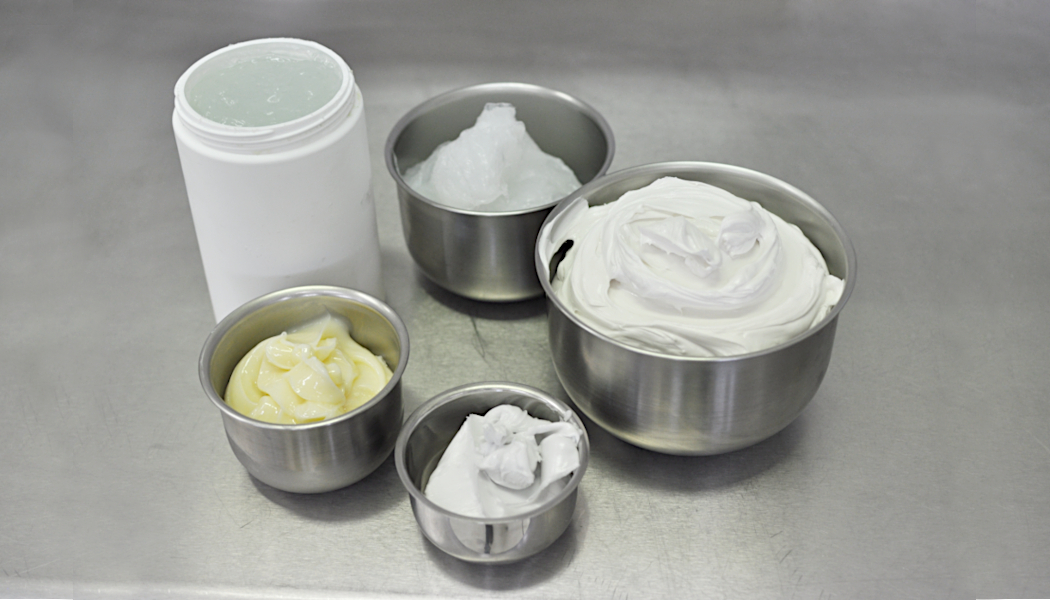

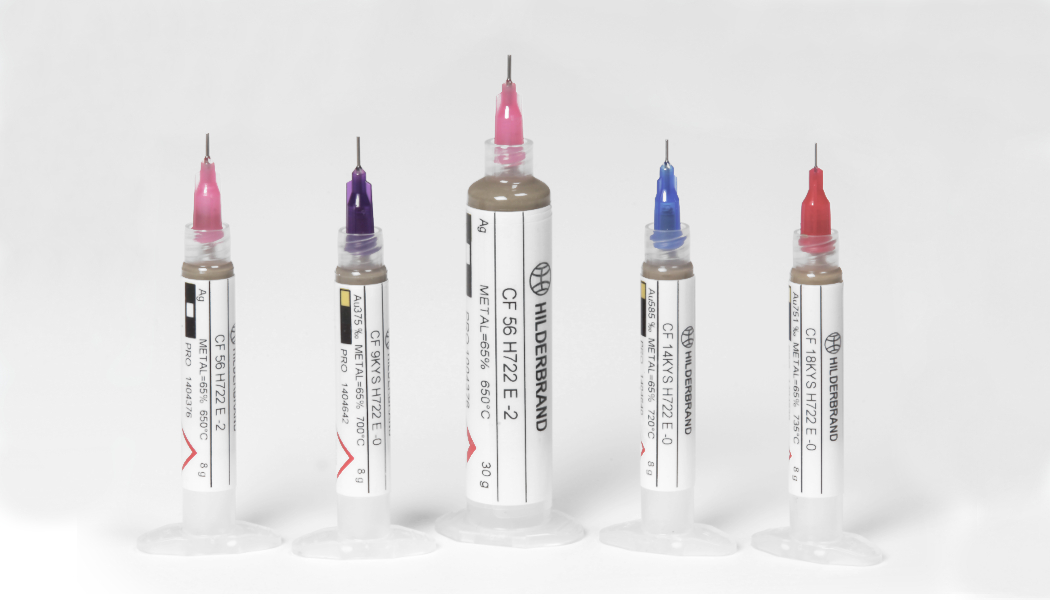
Pastes
Brazing pastes are often also called soldering pastes. They are a homogenous mixture of brazing alloy powder with a binder and, in certain cases, with a flux, depending on the heating technique. The alloy powder has the function of melting at the desired temperature, filling the gap by capillarity and assuring the joint strength after solidification. The binder assures easy and consistent dispensing and decomposes upon heating without leaving a residue. A flux is added when the parts to be brazed are heavily oxidized or when heating is done in air.
Identification code of HILDERBRAND brazing pastes
1. CF/CNF: CF Cadmium free / CNF Cadmium & Nickel free
2. Alloy: refers to the list of brazing alloys
3. Color: refers to the list of brazing alloys
Y: Yellow W: White P: Pink R: Red
4. Working temperature: refers to the list of brazing alloys
H: Hard MH: Medium-Hard M: Medium S: Soft ES: Extra-Soft
5. Flux binder / binder:
For torch: H722,H822,H511,P301,LR04
For resistance & induction heating: H122,H9129,X108
Controlled atmosphere: H300,H350,H400,H600,H700,H910,P300,LR00
Vacuum furnace: H800
6. Alloy powder content:
For torch, resistance & induction heating: E 65% / J 78%
For furnace under protective atmosphere: R 89% / T 91% / W 94%
7. Particle size
2: Standard 1: Fine 0: Extra-fine

